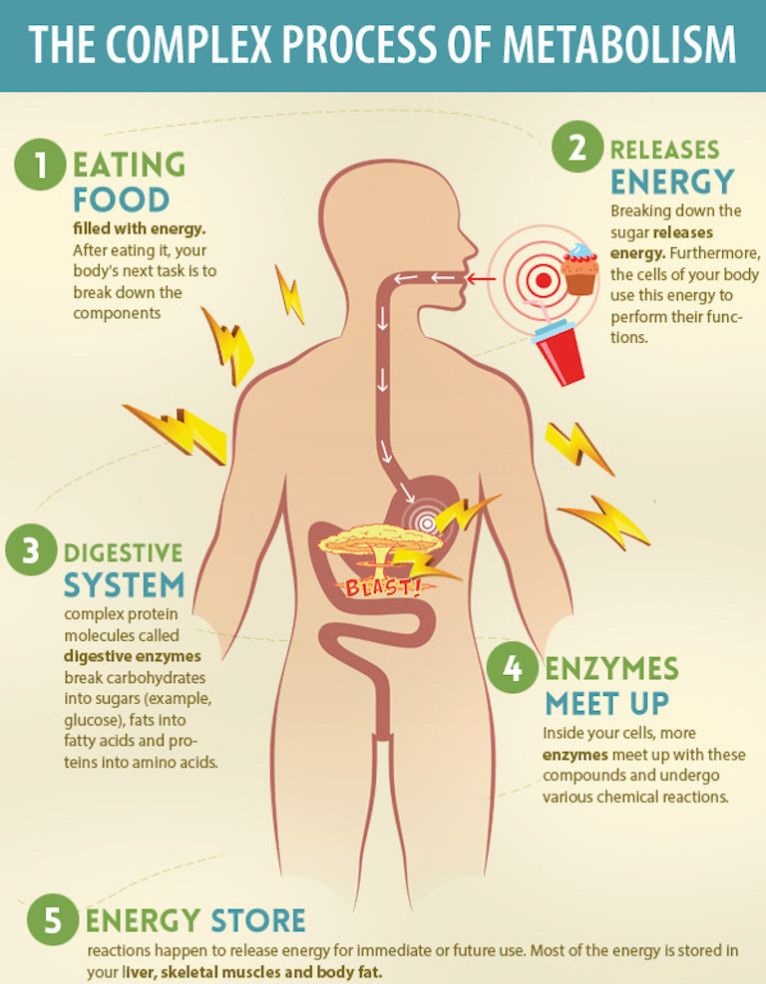
Every part of your body needs energy to function―whether its pumping blood to your heart, sending infection-fighting antibodies to a wound or helping your lungs draw breath. And this energy comes from the food you eat or drink measured in calories or kilocalories.
1 Kilocalorie is the quantity of heat required to cause a rise in the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 degree Celsius. The human body converts food into heat energy every day in order for you to survive.
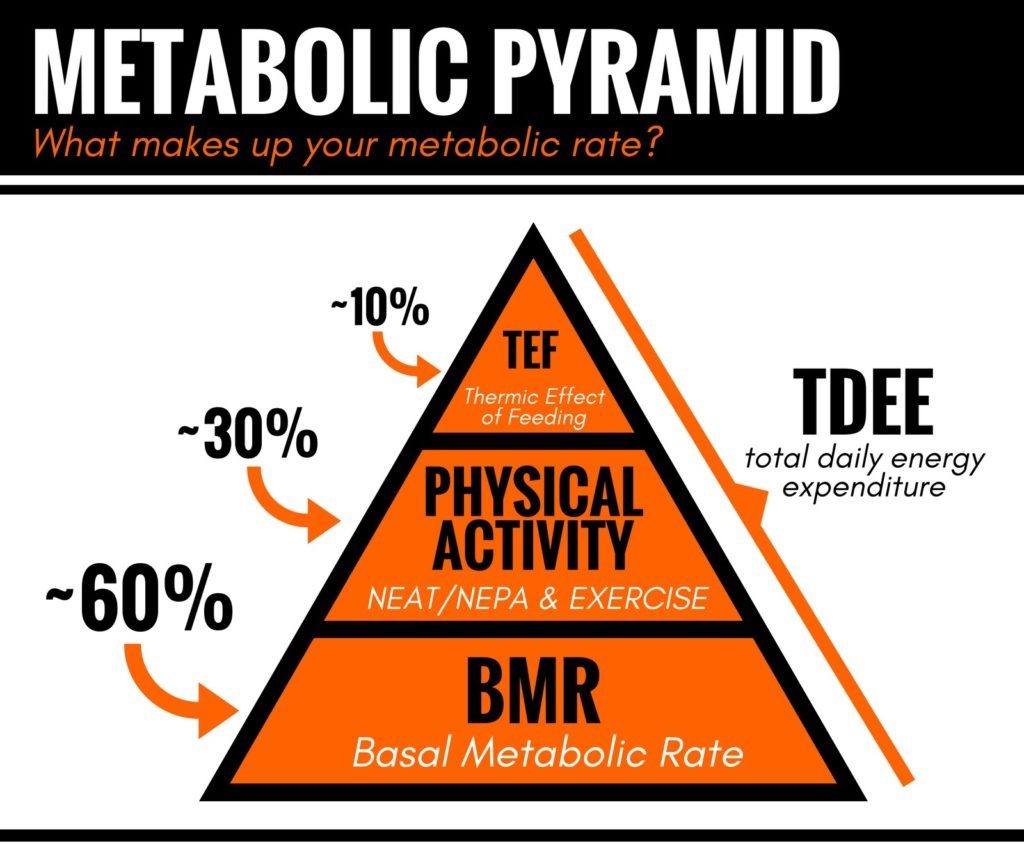
There are 3 components to your body’s total daily energy expenditure:
- Thermic effect of food: Amount of energy you spend digesting the food you intake
- Physical activity: Calories burned throughout the day whether it’s through exercise, sitting at your desk at work, doing some gardening, etc
- Basal Metabolic Rate: the number of calories you will burn while at rest.
The thermic effect of food rises after you eat and is at its peak 2-3 hours afterward. This effect depends on the food you eat and how much of it you eat for example:
- Fats increase the BMR which ranges from 0–5%
- Carbohydrates cause an increase of 5-10%
- Proteins increase the BMR from 20–30%
Energy expenditure during physical activity only makes up 20% of the total expenditure but may increase in case of strenuous exercise. This varies from person to person based on the nature of the activity, weight, age and intensity. Some examples (n kJ per kilogram per hour):
- Driving a vehicle – 3.8
- Walking fast – 14
- Swimming – 33
As for the BMR, we will take a deep dive into it in this article:
So what metabolism actually means?
When most people talk about metabolism, they are talking the BMR which is the number of calories you burn by doing no external physical activity. Everyone has a different BMR and it is a calculation based on age, weight, height and gender but also your nutrition and physical activity.
By understanding your basal metabolic rate, you can calculate the number of calories you need to consume in a day to keep your body moving. You can calculate your approximate BMR through the below formulae:
English BMR Formula
For Women: BMR = 655 + (4.35 x weight in pounds) + (4.7 x height in inches) -(4.7 x age in years)
For Men: BMR = 66 + (6.23 x weight in pounds) + (12.7 x height in inches) -(6.8 x age in year)
Metric BMR Formula
For women: BMR = 655 + (9.6 x weight in kilos) + (1.8 x height in cm)- (4.7 x age in years)
For men: BMR = 66 + (13.7 x weight in kilos) + (5 x height in cm) -(6.8 x age in years)
BMR makes up about 60% of your total energy expenditure. And if you were to consume this amount of calories without doing anything, you would not put on weight. In real life, we don’t just lie in bed and do nothing. Therefore, the activity level is also a factor in BMR calculations.
Figure out your activity level by choosing any of from below:
- No exercise- 1.2
- Lightly active (exercise 1-3 days a week)- 1.37
- Moderately active (exercise 3-5 days a week)- 1.55
- Very active (exercise 6-7 days a week)- 1.725
- Extremely active- 1.9
Multiply your BMR with activity level to get the number of calories you need to maintain your weight.
Understanding 3 different body types and their metabolism
Your genetics predisposes you to one of the three body types:
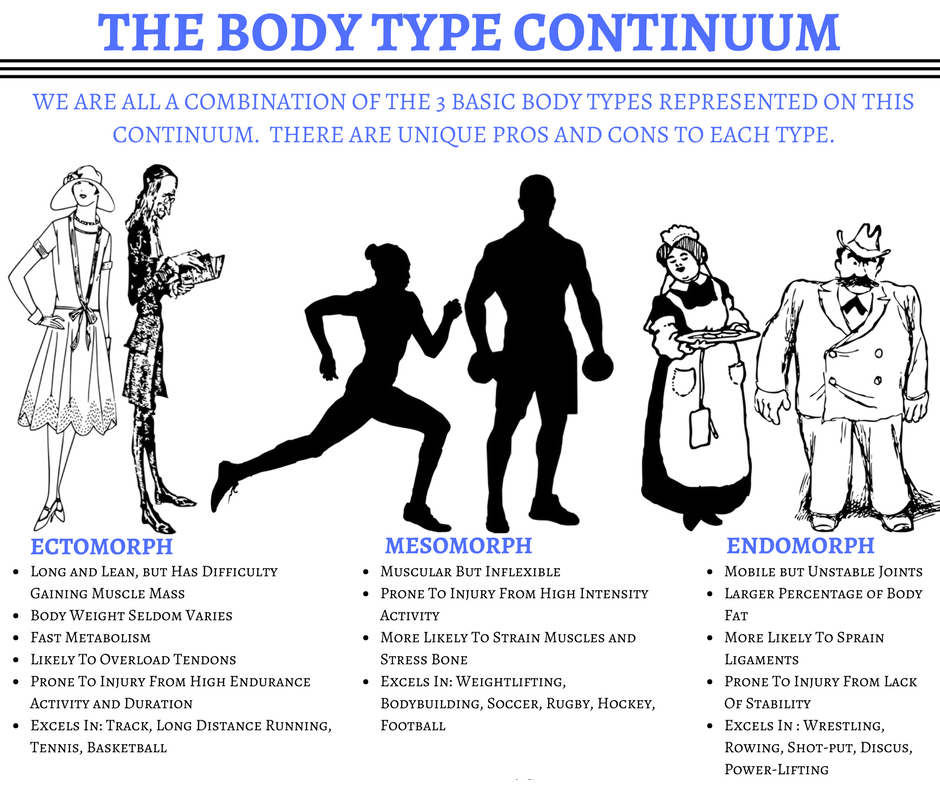
Ectomorph
They are your typical endurance athletes or skinny people.
They are characterized by
- Smaller bones structure
- Thinner limbs
- Shorter upper body, long legs and arms
- No real difference between the size of the hips, waist and shoulders
- Little fat storage
- High metabolism which makes it difficult to gain weight
The typical goal of Ectomorphs is to gain weight and muscle and this can be achieved by following a high carb, moderate protein and minimal fat diet.
A good foundation to start with is consuming 2-2.5g of carbs and 1.5g of protein per pound of body weight. Since metabolism is very high, we recommend eating something every 2-4 hours.
This should be combined with exercise with a focus on strength training for 4-5 sessions per week. You should ideally train with moderate to heavy weights with long rest periods of 1-2 min per set.
Focus on compound movements to build muscle mass and gain strength. Reduce cardio to 15-20 min sessions 2-3 times a week. Treat cardio as your warmup to avoid spending too much energy in the beginning.
Mesomorph:
They are characterized by
- medium-sized bones structure
- Athletic body
- Proportionate body with a good amount of lean muscles
- High metabolism but lesser than ectomorphs
- Easy to maintain a healthy weight and gain muscles
The typical goal of Ectomorphs is to lean up by reducing body weight and increasing lean muscles. As for their food intake, there should be a balance between carbs, protein and healthy fat.
As for exercise, they should focus equally on cardio and strength training combining both compound and isolated movements. Isolated movements are important if you’re looking to define and shape muscles in an aesthetic manner.
We recommend going for moderate or heavyweights with a moderate 30-90 sec rest between sets. Aim to perform strength training and cardio 3-4 times weekly.
Endomorph:
They are characterized by
- larger bones structure
- Soft body appearance
- Naturally curvy
- Slower metabolism thus they gain weight quickly
The typical goal of Endomorphs is to lose weight by following a low carb, high protein, and moderate fat diet. They should aim to eat regularly with lower portions to keep the metabolism high.
As for workouts, they should focus on interval and circuit training. Include compound movements with short rest between sets to burn more calories and build lean muscles. Go for moderate weights and include superset training. This is when you perform 2 exercises back-to-back without resting as this will help shed fat quicker.
Cardio should be the core of their training with a mix of strength training. Aim for 2-3 sessions of strength training and 4-5 sessions of cardio per week. Strength training will help to build muscles and increase metabolism.
Factors that affect metabolism

If you have tried any body composition machines, you might have seen a column for BMR. It means the minimum amount of energy required to sustain your life and keep your vital organs functioning while you’re at rest
BMR does not include daily physical activity and does not include physical activity or the energy you burn while eating food. So it only measures energy burnt while at rest.
If you want to know your BMR, you can try a body composition machine or you can use a BMR calculator online. 7 major factors affect your BMR:
- Psychological state: Stress and anxiety can have a massive increase in energy expenditure. When a person is ‘on-edge’, their body goes on alert mode. Different hormones circulate the blood vessels and communicate for them to break down energy stores
- Lean Body Mass: Muscle tissue has a higher metabolic rate compared to a fat tissue
- Gender: BMR of women is generally lower than men as they possess higher fat and less muscle mass.
- Age: Lean muscle mass generally decreases as you age causing a lower BMR. If an older person is obese, he/she will find it more difficult to lose weight compared to a younger person of the same weight
- Body temperature: If you have a fever, your body’s metabolism will increase as well as the thermogenesis
- Energy restriction: If you are eating fewer calories than usual or are on a diet, your body will conserve energy because it thinks you are in a starvation mode. This will decrease your metabolic rate
- Endocrine system: Hypothyroidism or under-active thyroid will cause you to decrease your metabolism and lead to weight gain. Hyperthyroidism or an overactive thyroid will cause you to increase your metabolism and leads to rapid weight loss.
- Hereditary: Many factors contribute to your metabolism level, the major one being heredity.
Metabolism and Genetics
Think of your genes as a library book. Your test results will depend on how you reference a book and what you do with it. Different people in the class will get different results.

50% of weight gain or loss is your lifestyle and how you choose to live your day today. The environment your genes are in such as the stress you face, exercise, how much you sleep create a different interpretation of the genes or the ‘book’.
Your ancestors can be blamed for your metabolism only if you’re looking for someone to pass the buck. When your ancestors figured out how to survive, they left this experience in the form of genetic marks in your DNA which has passed on to you.
So if your ancestors didn’t get fast-food in their time, your body will not know how to respond properly.
At the end of the day, you cannot give up on fitness blaming your family. You have to consider the way your ancestors lived their life and the way you are.
Metabolism and aging
The average human will see a 1-2% decrease in Basal Metabolic Rate every 10 years which makes us 50-70% of your total metabolism. Every decade after your turn 30, you will see a 1-2% decrease in BMR.
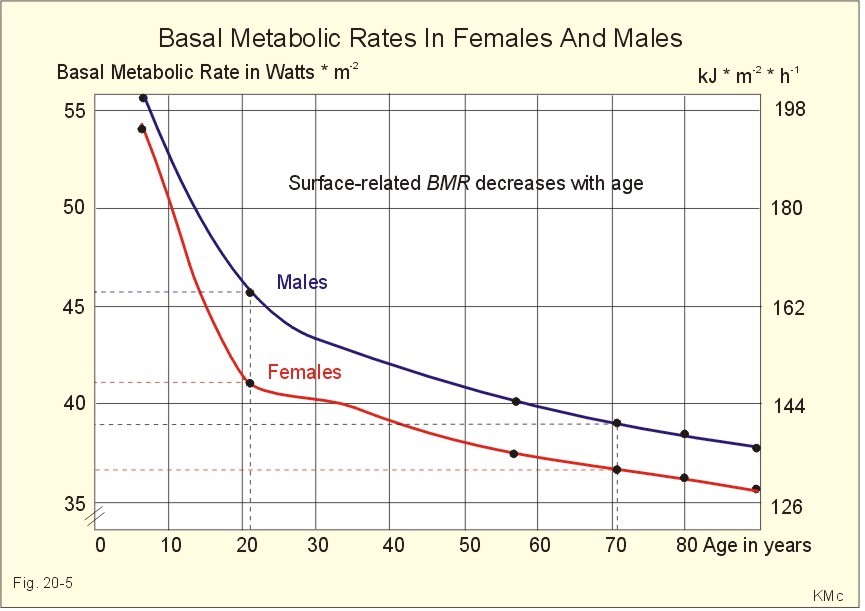
Most people over the age of 30 begin to blame their metabolism in case they gain weight. As you can see a decrease of 1-2% cannot be the sole cause!
As we get older, we’re less prone to moving and doing physical activities and that’s probably the biggest contributor to your metabolic slowdown.
Metabolism and it’s regulation in our body
The Thyroid gland is a small gland present in the front of the neck or just below a man’s Adam’s apple. The major function of this gland is to transform iodine found in the food you take and convert into 2 hormones- thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Small amounts of iodine are present in food, especially seafood. Otherwise, it is added into the salt we eat and is sufficient for the body.
Only thyroid cells can transform iodine. Thyroid cells mix iodine with tyrosine, an amino acid, to make T3 and T4 which are released into the blood. They travel all through the body and regulate metabolism.
So the fact is that every part of your body depends upon thyroid for the regulation of their metabolism. A normal thyroid gland will make 80% T4 and 20% T3 but T3 has 4 times the strength of T4.
Effect of food on metabolism
While it may seem too good to be true, you can eat your way to a fit and lean body. With the right choice, you can actually increase metabolism and burn fat with the food you eat.

The thermic effect (energy required to digest food) can be amplified by your food choices such as:
Beans
They contain protein, fiber, and iron that helps in boosting metabolism. Protein triggers more calories to be burned.
Hot peppers
Hot Peppers like jalapeno, cayenne pepper, ginger, and ground chili are great for boosting metabolic activity. They contain a chemical called capsaicin that is responsible for increasing metabolism. Also, hot peppers reduce appetite and keep you full for longer bringing about weight loss. The seedier and pungent spice, the better it is for metabolic activity.
Citrus Fruits
They are rich in vitamin C which aids fat burning effects and boosts metabolism. Vitamin C also balances insulin levels, reducing spikes that cause carbohydrate cravings.
Dark chocolate
With 70% or more concentration of cacao dark chocolate contains magnesium, a mineral known to incentivize the metabolic process to speed up.
Cinnamon
It not only has a great flavour but also contains thermogenic properties that burn more calories throughout the day.
Salmon
Salmon contains a high quantity of omega-3 fatty acids and protein. This works together to boost the metabolic process. Omega-3 fatty acids lower blood sugar also.
Green tea
It contains epigallocatechin gallate, a form of catechin, which has been proven to enhance the fat-burning process.
Broccoli
It is a fat-fighter due to several detoxifying vitamins like A, C, antioxidants, dietary fiber and folate. All of these play an important role in weight management and cleansing process.
Berries
Berries are rich in anthocyanins which encourage the production of the hormone adiponectin which prevents the expansion of fat cells. Berries such as strawberries and raspberries are rich in polyphenols which can reduce the body’s absorption of starch and fats.
Garlic
It has been linked to higher testosterone levels which are closely related to energy production. More energy means you will be more physically active and be more likely to maintain healthy body weight.
Protein
Protein causes your body to work harder to digest it and you will burn more calories consuming it than ordinary foods
Metabolism types – Fast and Slow
Think of your body as a car and the engine is the metabolism, which determines how much fuel is used up like metabolism.
If you have a fast metabolism, you will burn more calories at rest and during any physical activity. Since more calories are burnt, you will need to eat more to maintain your energy. This is why you may have noticed some people being lean even after consuming a lot of food.
If you have a slow metabolism, you will burn fewer calories at rest and during physical activity. To lose weight, you will have to consume much less than normal. Slow metabolism may be due to diseases like hypothyroidism, PCOS, pituitary disorder and Cushing’s disease.
Understanding Cell Metabolism
Many people have this vague idea that metabolism has something to do with weight loss. This is partly true as the study of metabolism does include research about how cells store, build and break down fat but metabolism is far more interesting than weight loss trends in the news.
Metabolism is so important that several of the chemists working with NASA believe that the study of metabolism can help us understand the origins of life itself.
Your cellular metabolism consists of hundreds of different reactions. To make sense of them all, researches break them into 2 categories:
- Anabolic Metabolism: reactions that join molecules together to build new ones
- Catabolism: reactions that break molecules apart
When you eat a banana, your digestive tract processes it and reduces it to molecules of fats, glucose, fats, and amino acids. Intestines absorb them and they then enter the bloodstream to be distributed to the cells of your body.
Once inside the cell, metabolic reactions take place transforming the molecules.
A cell’s metabolism, its internal network of chemical reactions, takes molecules from the environment (the molecules of an apple in this case) and transforms them into pieces of the cell itself.
Sometimes the cell builds replacement parts for its molecules that have been worn out. Other times it builds energy molecules. These are fuel and give energy for future activities of the cell. Muscle cells use energy molecules to expand, brain cells use them to instruct organs to work and so on.
In summary, cellular metabolism can be defined as the total of all controlled chemical reactions that occur in a cell.
Metabolism and Muscle Mass
Muscle has many hidden effects on metabolism. When you’re done exercising especially after a weight-training session, your body needs time to return to homeostasis.
It needs time and energy to refill the depleted glycogen stores in your muscles and for more protein-turnover. So the assumption that muscle itself burns a ton of calories at rest is probably not true.
However, muscle after the influence of training especially weight training and high-intensity training burns more calories in the recovery process.
So if you’re not exercising, definitely try to incorporate strength-training or high-intensity interval training to increase the number of calories you burn at rest.
We don’t know the full-story of muscles but we do know that it does influence your resting energy expenditure.
In a study called ‘age-related decrease in resting energy expenditure’, we get a glimpse of what causes a slowdown in metabolism we see as people get older. A lot of people believe that as we grow older our metabolism naturally slows down and there is nothing we can do about it. But this may not be as true as we once thought.
The results suggest that a loss of muscle mass as we age, especially leg muscles can lead to a decrease in resting energy expenditure. This study also acknowledges that the decrease in resting expenditure changes are not fully explained just by changes in the body composition. There are other factors at play here.
But if you want to improve and increase your metabolism, there is a huge correlation between healthy body composition and a higher basal metabolic rate. The more lean mass you have the higher your metabolism will be.
Even if it is not a drastic change, it’s one of the few ways you can improve your metabolism. Also as you get older, you should try to do everything you can to avoid a decrease in metabolism by maintaining as much lean body mass as you age.
There is also one other thing you can do to increase your metabolism such as the food you eat. The thermic effect of food changes based on what macronutrients you’re eating. For example, protein is harder for your body to break down than fats or carbs are. So it will require more energy for that protein source to break down. Eating a higher protein diet may help increase thermogenesis.
In a study that was done to comparing lean men to obese men- it found that
Body composition is a significant determinant of thermogenesis after eating. The bottom line of this study is that lean men use a lot more energy from the food they ate than obese men. Muscle mass itself at rest may not cause a drastic increase in metabolism. But when you combine the effect with a lean body mass on your energy-levels and on how you process and assimilate food, we start to see that muscle mass has a very big role in how many calories you burn per day excluding exercise.
In conclusion, we can increase our BMR to reach our fitness goals. Just because it is not as high as we want it to be now, doesn’t mean we can’t get to that level. All we have to do is make sure we get proper nutrition and are completing regular physical activity.
Metabolism FAQs
What is metabolism in the body?
Metabolism is a set of chemical processes that occur in a living organism to maintain life. In simple words, metabolism is the amount of energy released in any sort of activity such as digesting food we eat, while physical activity or even while resting
How does metabolism affect the 3 body types?
There are 3 body types namely ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph. Ectomorphs are typical endurance athletes or skinny people who have high metabolism. Mesomorphs are people with medium sized bones and lean muscle mass. They also have high metabolism which is little less than ectomorphs. Endomorphs are people with lowest metabolism who tend to gain more weight.
What affects metabolism?
Metabolism can be affected by a lot of factors including physical and mental situations. Some of these factors are Psychological state, Lean Body Mass, Gender, Age, Body temperature, Energy restriction, Endocrine system and Hereditary.
Is metabolism genetic?
Well the answer is yes, metabolism is partly genetic. However, you cannot blame everything on your genes or family because metabolism can surely be manipulated by changing one’s eating patterns and physical activities. Remember the quote “Fat doesn’t run in your family, nobody runs in your family!
Does age affect metabolism?
Yes, age is a crucial factor that affects metabolism. As you age, 1-2% decrease in Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) in every 10 years is noticed. This significantly increases after you are 30. Also when you age, there is a noticeable decrease in physical activity for most of the people which decreases metabolism.
How does the body regulate metabolism?
Metabolism in our body is regulated by thyroid gland present at the frontal area of neck or right below where a male’s Adam apple is. Thyroid gland converts iodine we consume into 2 hormones- thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). T3 and T4 travel throughout our body through blood and regulate metabolism.
What foods boost metabolism and burn fat?
The energy required to digest food i.e The Thermic Effect can be increased by right choice of foods we eat such as beans, hot peppers, citrus fruits, dark chocolate, cinnamon, salmon, green tea etc. Higher thermic effect leads to higher metabolism rate.
What are the two types of metabolism?
The two types of metabolism are fast and slow. In fast metabolism, you will burn more calories at rest and during any physical activity. In slow metabolism, you will burn less calories at rest or during physical activity.
How does cell metabolism work?
Cell Metabolism can be divided into 2 main types namely Anabolism and Catabolism. Anabolism or anabolic metabolism can be defined as reactions that bind molecules together to build new ones. Catabolism or catabolic metabolism can be defined as the process of breaking molecules apart.
Does increasing muscle mass increases metabolism?
Yes increase in muscle mass will increase metabolism as muscle movements in our body use more energy that fat. However, muscle mass alone at rest can’t be a major factor to increase metabolism.